A Beginner’s Guide to Developing a Successful Fintech App

Table of Contents
Fintech, or financial technology, changes how we manage, invest, and spend our money. The financial sector and modern technology work together to offer safer, quicker, and more intelligent ways to handle resources and transactions.
Global innovation is behind the fintech industry's explosive rise. This vibrant sector, which includes digital payments and cryptocurrencies, is changing economies and creating new business models that have exciting possibilities.
Fintech is a group of technologies and services that enhance financial services, not a just one thing. Among the important types are:
- Digital Wallets & Payments: Simplifying the money transfer process.
- Lending Platforms: Connecting lenders with borrowers, frequently at more favorable rates.
- Insurtech: Bringing faster claims processing and more individualized insurance to the insurance sector.
- Robo-Advisors: Providing automated investing guidance that may be tailored to your specific needs.
Our financial habits have changed as a result of the growth of fintech apps. In addition to being well-known, apps like PayPal, Stripe, Robinhood, and Revolut have expanded the options available to both individuals and companies. These applications' innovative solutions to practical financial issues, simplicity, reduced costs, and more transparency have led to their enormous success.
There is a lot of room for expansion when creating a financial app nowadays. There is a growing need for creative solutions as more customers use digital services. Making a fintech app may lead to a profitable market, regardless of your goals—improving user experience, educating people about finance, or simplifying intricate procedures.
Insufficient financial literacy is one of the most urgent issues facing the financial industry. Through the provision of investing platforms, budgeting tools, and instructional materials, fintech applications are closing this gap and enabling everyone to understand complicated financial concepts.
With open banking, third-party applications may safely access banking data and offer users customized financial solutions, sparking a surge of innovation. Along with increasing competition, this approach also allows customers more financial autonomy.
Mobile devices are the center of fintech's explosive growth. The global economic environment has been revolutionized by mobile penetration, which has already reached new heights by placing financial services in the hands of billions of people.
Key Functional Domains of Fintech Apps
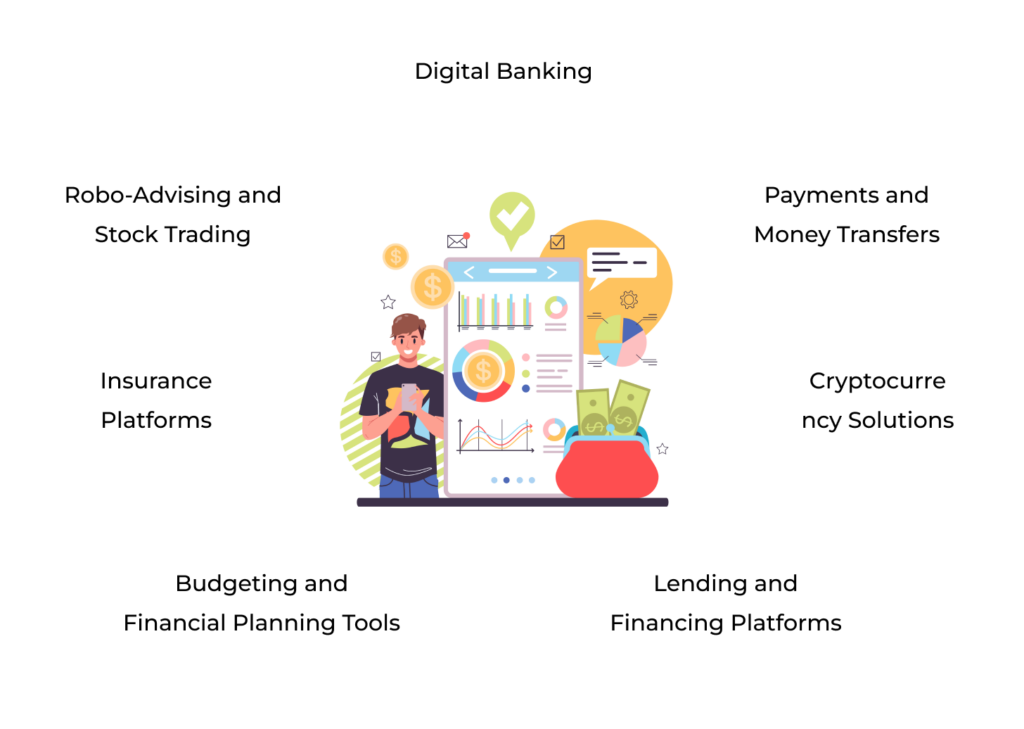
Digital Banking: Redefining Traditional Banking
From basic Internet banking, which offers a variety of services without requiring a physical bank branch, such as check and savings accounts, loans, and credit features, digital banks have developed into the whole economic ecosystem. The pleasant user interfaces, affordable prices, and improved customer support of these programs provide users more control over their financial operations.
Payments and Money Transfers: Simplifying Transactions Across Borders
The days of lengthy therapy for financial gain are passed. Make the Fintech application quick and affordable in the payment area, whether you're paying for services overseas or sending money to a buddy. Thanks to the rise of apps like Venmo, PayPal, and Wise, customers can now transfer money with lower fees and more security.
Cryptocurrency Solutions: A New Era of Digital Assets
Ahead of the cryptocurrency revolution that is changing the economic landscape is the Fintech application. Applications like Coinbase, Binance, and Crypto.com offer intuitive user interfaces for interacting with cryptocurrencies, whether for investing, acting, or securely storing digital assets. These platforms have made it possible for users to use blockchain technology and digital currency more than before.
Robo-Advising and Stock Trading: Investing Made Easy
The financial sector is being transformed by robot suggestions, which offer algorithm-operated guidance and portfolio management. With the help of fintech apps like Betterment, E*Trade, and Robinhood, stock traders can now manage their ownership interests in investments more conveniently and often for free. With these gadgets, users may make more informed investments without needing to be very skilled in finance.
Insurance Platforms: Smarter Coverage for a Smarter World
Fintech has expanded the insurance industry by creating, managing, and even simplifying insurance needs through apps. Platforms such as Lemonade and Oscar Health combine AI and automation to offer customized insurance experiences that make cost reduction, plan comparison, and political interpretation easier.
Budgeting and Financial Planning Tools: Empowering Financial Literacy
Though it can still be difficult, the strong budgeting and financial planning capabilities of fintech apps are making money management simpler. Apps such as Mint, YNAB (You Need A Budget), and Personal Capital allow users to organize their spending, set savings targets, and monitor their assets all from one place. In addition to providing information to help users achieve their financial goals, these tools encourage better financial behaviors.
Lending and Financing Platforms: Connecting Borrowers and Lenders
With its ability to provide rapid and easy funding without the need for conventional financial intermediaries, lending platforms have revolutionized the financial industry. By bringing borrowers and lenders together online, apps like LendingClub, Kiva, and Upstart are revolutionizing the loan industry and frequently providing better conditions than banks do. These technologies facilitate easier finance access for both people and enterprises.
Our Complete Guide to Building a Fintech App will equip you with the strategies, insights, and tools needed to create a powerful, secure, and seamless financial solution. Don’t just build an app—build a game-changer. Start your fintech journey now!
Core Features of Fintech Applications
Security Features: Trust and Protection First
Security in the financial sector is absolutely necessary. Strong encryption should be given high priority in fintech apps, two-factor authentication (2FA), biometric verification (such fingerprints or facial recognition), and safe data storage. By guaranteeing that sensitive financial information is shielded against infringement, these attributes boost consumer trust and loyalty.
Payment Integration: Smooth Transactions at Your Fingertips
It should be possible to integrate payments whether you are sending money, paying bills, or shopping online. Many payment channels, like Stripe, PayPal, and Apple Pay, are integrated by fintech applications to give users quick, secure, and varied payment choices and to enable more impromptu and efficient transactions.
Machine Learning and Predictive Analytics: Smart Decision-Making
Fintech is changing because of data-driven insights provided by machine learning and predictive analytics. These functions enable applications to make more informed financial decisions, warn users of possible dangers, and provide tailored suggestions by examining spending, investing, and saving behaviors. These tools are used, for example, by Monzo and Chime to provide real-time financial advice.
Interactive Dashboards: Simplified Financial Management
Interactive, user-friendly dashboards make it simple to see a person's financial situation visually, including graphs and key performance indicators. Monitoring investments, savings, costs, and other activities is made simple for users by this dashboard. Giving people complete control and transparency over their financial life with no effort is the goal.
Voice Integration: Hands-Free Banking
With the rise in popularity of voice assistants like Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri, speech integration in banking applications is becoming more and more important. Voice commands enable users to carry out tasks like transferring money, paying bills, and checking bank account balances while utilizing spoken language. Accessibility and usefulness are enhanced by this hands-free feature.
Advanced Technologies Shaping the Future of Fintech:

Artificial Intelligence (AI): The Brain Behind the Operations
Artificial intelligence is transforming the economic business through advanced decision-making, system optimization, and task automation. AI-powered tools like chatbots, fraud detection algorithms, and robo-advisors (including those employed by Wealthfront and Betterment) have the potential to offer personalized financial advice, identify anomalies, and improve the efficiency and usability of services.
Digital Analytics: Data That Drives Financial Insights
Fintech businesses may get useful insights from massive volumes of data thanks to digital analytics. Fintech applications may enhance user experiences and provide personalized suggestions by examining transaction data, user behavior, and market trends. Financial institutions are able to swiftly adapt to changing client requirements and improve their services because to this data-driven strategy.
Blockchain: Transparent and Secure Transactions
Blockchain technology provides security and transparency never before possible. A distributed ledger and transaction decentralization are two ways that fintech apps might increase confidence in financial transactions. Blockchain-based applications, like Ethereum or Ripple, provide enhanced trust and immutability, making them perfect for smart contracts and cryptocurrency trading. They also enable quicker and less expensive cross-border transactions.
Big Data: Unlocking Insights from Massive Datasets
Fintech apps have the ability to process and evaluate enormous amounts of financial data from several sources in real time, leading to big data. Additionally, businesses may use this technology to predict trends, customize services, and identify customer behavior. Fintech companies may also employ massive data to provide consumers personalized responses, threat evaluations, and unique financial projections.
Developing a Fintech Application
The process of developing a fintech application is both thrilling and challenging, requiring careful planning, selecting the right technologies, and overcoming important obstacles. Here's a thorough look at the procedures and factors to aid you along the way while developing a profitable fintech app.
Steps to Create a Fintech App:
Research and Define Product Requirements: Laying the Foundation
The first stage is to do extensive research to identify the proper financial issues your app aims to address. Comprehending your target audience, the financial services you want to provide (such as payments, investments, coverage, and so on), and the essential features that will set your app apart from the competition are all essential for this. At this stage, it is important to clearly define the app's objectives, user needs, and relevant laws. The development process will go more efficiently the more unique your needs are.
UI/UX Design Considerations: Creating an Intuitive Experience
Any financial software's design is essential to attracting users. To keep users interested and ensure they can use the app without any issues, a user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) are important. Readability and simplicity are important since fintech apps often deal with sensitive financial information. When designing, some things to think about are:
- Clear visual hierarchy and clean layouts
- Easy navigation between financial tools and options
- Accessibility features (font size, color contrast, voice support)
- High security assurance through visible icons and features A great design is not just aesthetically pleasing, it should also provide a frictionless experience for users.
Choosing the Right Tools and Languages: Picking the Right Tech Stack
The performance, scalability, and user experience of your project will be determined by the tools and languages you use. Selecting technology that provide security, scalability, and seamless operation is crucial for fintech. Fintech apps often use the following tech stacks:
- Frontend: React Native, Flutter (for cross-platform development)
- Backend: Node.js, Python, Ruby on Rails
- Database: PostgreSQL, MongoDB
- Blockchain: Ethereum, Hyperledger (if using blockchain features)
- Cloud Services: AWS, Google Cloud (for scalability and security) Choosing the right tech stack depends on your app’s complexity, scalability requirements, and expected user base.
Development for iOS and Android: Platform Considerations
Whether to create a cross-platform solution or a native app for iOS or Android will be your decision. Although native development provides superior user experience and performance, it can be expensive and time-consuming to construct both versions independently. With cross-platform frameworks like Flutter or React Native, you can keep a single codebase for both platforms, which may save money and time during development.
Although the coding may be the same, keep in mind that you must follow the unique UI requirements of each platform.
Challenges in Development: Navigating the Complexities
Given that fintech apps have to follow strict financial regulations specific to their services and geographical areas, regulatory compliance is a significant challenge. GDPR for users in Europe, KYC and AML rules, and national legislation such as the Dodd-Frank Act in the United States are all examples of this. If you don't follow the rules, you risk harsh penalties, legal action, and losing users' confidence. Consulting legal professionals in advance guarantees that the software satisfies all criteria.
The sensitive nature of financial data makes data privacy and security equally important. To stop fraud or breaches, apps need to use safe authentication techniques like two-factor authentication, execute frequent security audits, and use robust encryption. PCI DSS requirements must be followed while processing payments in order to preserve user privacy and confidence.
Performance and scalability are important for long-term success. Fintech apps need to effectively manage growing transaction volumes and data traffic as their user base expands. While a microservices design enables the autonomous scalability of various functionality, cloud-based platforms like AWS and Google Cloud offer flexibility. Even at times of high demand, load balancing and optimized databases provide seamless operation, avoiding lags or interruptions in service.
Create an app that not only meets the needs of today but shapes the future of healthcare. Start building solutions that truly make a difference!
Factors Influencing Fintech App Development
Careful planning, resource allocation, and post-launch assistance are necessary while creating a financial app. Its success is greatly influenced by the price, schedule, and continuing upkeep.
The complexity of the program, the location of the development team, and the technological stack are some of the variables that affect the development cost. Costs are further increased by advanced features like blockchain integration, AI-powered financial tools, and payment processing. Costs are also impacted by whether to build for iOS and Android natively or cross-platform, with frameworks like React Native or Flutter potentially saving money. While outsourcing nations like India or Eastern Europe may save expenses, they may also present communication or time zone issues. Development teams in areas like the United States or Western Europe often charge more. Fintech apps also need to strike a balance between security and usability, which affects the total cost.
It usually takes six months to more than a year to build, depending on how complicated the software is. planning and research (1–3 months) are needed to establish the process's objectives, features, and compliance standards. After that, there is Design and prototyping (2–4 months) with an emphasis on security and UI/UX. If more complex features like AI, blockchain, or multi-platform compatibility are needed, the frontend and backend coding for the actual app development (4–12 months) takes longer. Security, performance, and regulatory compliance are guaranteed before launch through testing and quality assurance (2–4 months). Lastly, launch and marketing (1–2 months) include promotional plans and app store approvals.
Maintenance after launch is important for sustained performance. Frequent bug fixes, security patches, and updates enhance performance and guard against online dangers. Customer retention and attraction are helped by feature improvements based on user input, and scalability guarantees that the app can manage increasing transaction volumes. Keeping up with regulatory changes is essential for compliance, and offering dependable customer service increases consumer pleasure and confidence.
Monetizing Your Fintech App: Turning Innovation into Revenue
Selecting the appropriate revenue model is the next step after developing your financial app to guarantee long-term success. The characteristics of the app, the intended user base, and corporate goals all influence the optimal strategy.
Using a freemium model or tiers of plans to offer premium services, a subscription-based strategy generates consistent revenue. Basic tools are free for anyone to use, but more complex services like financial advice or investment tracking need to be upgraded for a fee. Additionally, some applications utilize a pay-per-use business model, charging users for particular premium features. Investment platforms, trading applications, and personal finance tools all benefit from this strategy.
Fintech apps that manage payments, transfers, or investments can also be profitably monetized through transaction fees. Apps have the option to collect a nominal fee for each transaction, which may be expressed as a percentage of the total or as a fixed rate. Trading applications make money from transaction fees or bid-ask spreads, while foreign exchange platforms make money from exchange rate margins. With large transaction volumes, this methodology scales effectively.
Referral programs and advertisements may be quite profitable for applications that depend on a huge user base. The display of tailored advertisements for financial services or goods brings in money through clicks or impressions. Fintech applications can also get paid through referral programs when users join up for partner services like credit cards or insurance policies.
Data monetization is another possible source of income, but it must be done morally and in line with privacy regulations such as the CCPA and GDP regulations. Apps can provide aggregated, anonymised financial insights to banks, insurers, or market researchers in place of selling individual user data. While protecting user privacy, these insights assist companies in improving their offerings.
Finally, by providing access to financial tools like banking connections, fraud detection, and payment gateways, fintech apps may make money through referral and paid APIs. By integrating third-party financial services, fintech applications can generate commissions, or businesses utilizing these APIs can pay for access.
Advantages of Developing Fintech Apps
Innovations in technology and changing customer needs are driving the fintech industry's explosive expansion. Creating a fintech application improves accessibility and user convenience while also helping new companies in the financial services industry.
Consumers desire financial services that are quick, simple, and available around-the-clock. By being accessible 24/7 and allowing users to manage their finances without visiting a bank, fintech apps meet these demands. It enables quick and easy transactions, such as tracking investments, applying for loans, and transferring money. By offering customized financial data and recommendations, AI-driven customization improves the user experience even more. Fintech applications, which prioritize mobile-first approach, complement the modern digital lifestyle by simplifying and enhancing accessibility to financial management.
Fintech applications' ability to increase financial inclusion is one of their main benefits. Because of high entrance hurdles like income criteria or credit history, traditional banking institutions frequently reject people. Underserved people may now access vital financial services thanks to fintech solutions, which provide digital wallets, microloans, and alternative credit scoring models. Additionally, cross-border payments and digital transfers have been simpler, giving consumers all around the world financial connectedness. To help users make wise financial decisions, a lot of fintech applications also include financial education features.
The fintech industry is a highly attractive place for innovation and business growth. Blockchain, big data, and emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) are driving new business trends in everything from robo-advisors and peer-to-peer lending to crowdfunding platforms and digital-best banks. Since fintech has an untapped market, it offers businesses the chance to expand quickly, especially in underdeveloped nations with weak banking systems. Through open banking and API connectors, fintech programs may also collaborate with traditional financial institutions to increase their clientele and enhance their provider offerings.
The way companies and individuals engage with financial services is being revolutionized by fintech applications, which simplify transactions, promote innovation, and revolutionize financial accessibility.